Structure of the degree program
The content on this page was translated automatically.
Study profile
Within the wide range of styles offered, the teacher training course for grammar schools and the teacher training course for secondary modern schools give students the opportunity to develop their own artistic profile (classical, jazz, pop, etc.) in their main instrumental subject. The teacher training course for elementary school primarily teaches the basic techniques of practical instrumental playing in schools. Further focal points are school-related music-making, arranging and composing as well as musical-scenic project work, a special feature of the Kassel teacher training course.
The music education seminars and internships enable students to reflect on, plan and design music-related teaching and learning processes. In order to explore how music can be taught, it is important to reflect on the different perspectives of musical education, teaching and learning. In addition, new teaching concepts and real-life teaching situations are the subject of the course. In this way, theory and practice remain in a reciprocal exchange.
Music is made by people and for people. How this happens and why, what forms music takes and what meanings are assigned to it at different times and in different cultural contexts - these are questions that musicology at the University of Kassel explores. As a systematic and historical musicology, it offers different perspectives on its subjects and encourages students to reflect on the phenomenon of music.
Information will follow.
A particular focus is on popular music, with a dedicated professorship for this area. The focus here is on band playing, supplemented by practice-oriented courses in arranging/composing and the use of professional studio software.
With its diverse aspects and questions, the subject area of music theory stands side by side with the instrumental or vocal subjects as well as with musicology and music education courses. The central questions here are what "holds composed music together at its core" - be it from a purely acoustic, compositional, historical or stylistic perspective - how it is formed in detail and how we perceive it when we hear it.
In composition, students learn how to deal with compositional conventions and styles in such a way that they can become creative themselves. They compose their own stylistic copies, improvise practically on given material, establish references to original compositions and trace music-historical and aesthetic developments.
In analytical courses, the focus is on the examination of compositions of different genres and styles as well as the search for an appropriate way of speaking or writing about music. Analytical findings are not only related to academic questions, but are also made usable for the student's own musical interpretation. This broadens musical horizons and the listening repertoire.
In aural training, which is closely linked to the other areas, students reflect on their individual listening comprehension and their inner conception of sound. They develop methods to further differentiate this listening comprehension, process auditory impressions and apply auditory skills to aspects of their own music-making (rhythm training, sight-singing, listening for mistakes, replaying, etc.), but also to analytical questions.
In addition to the curricular courses (composition, aural training, analysis), supplementary courses are always offered in the subject area. Examples from current and past semesters: Interpretation criticism, music literature studies, open practice courses in aural training, didactics of listening education, composing from literary sources, practice courses in practical piano composition, basso continuo playing."
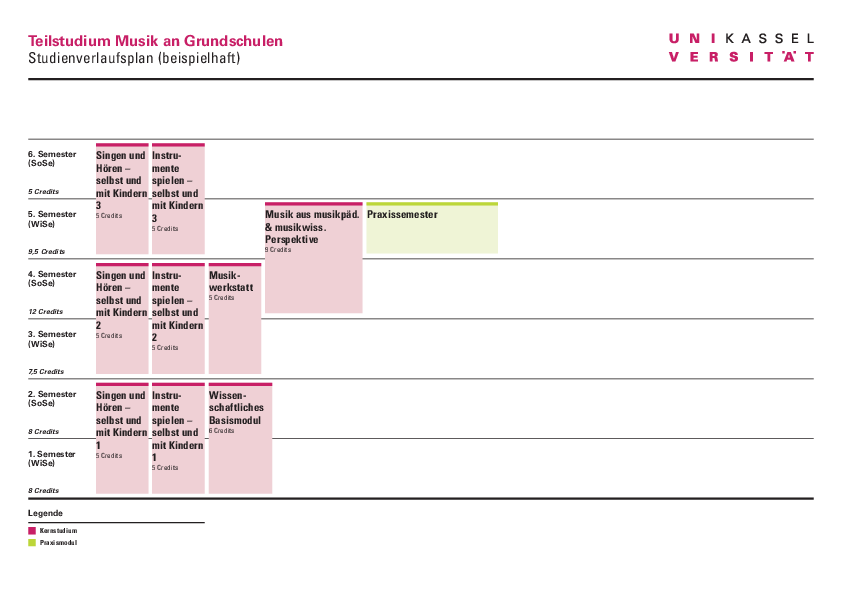
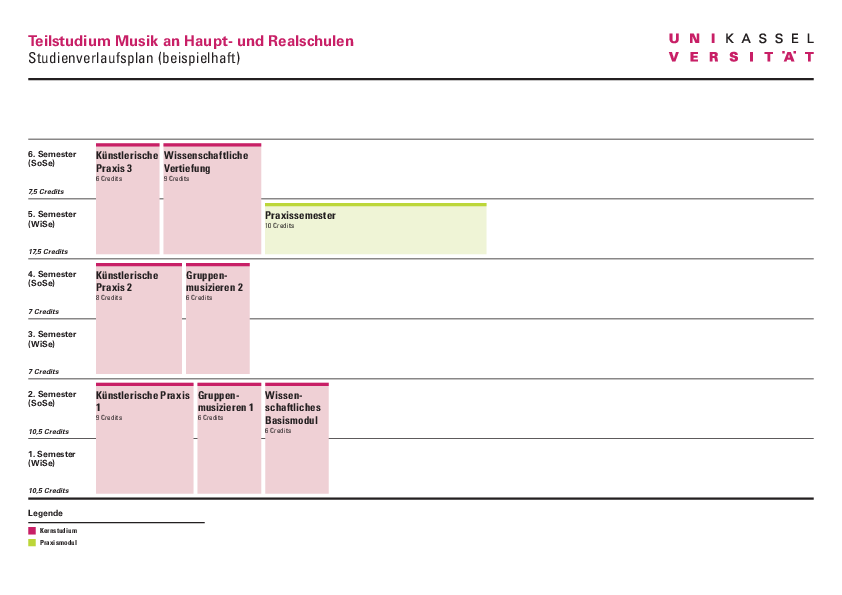
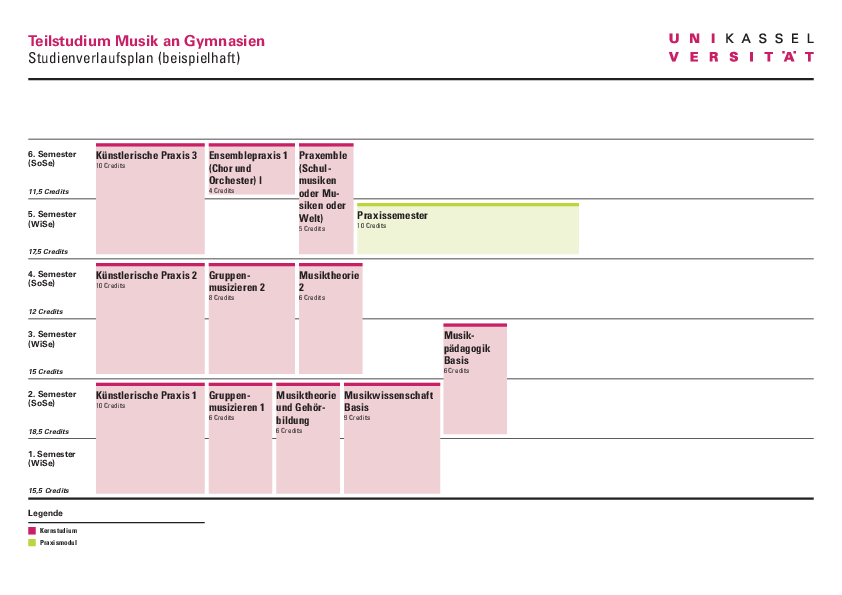
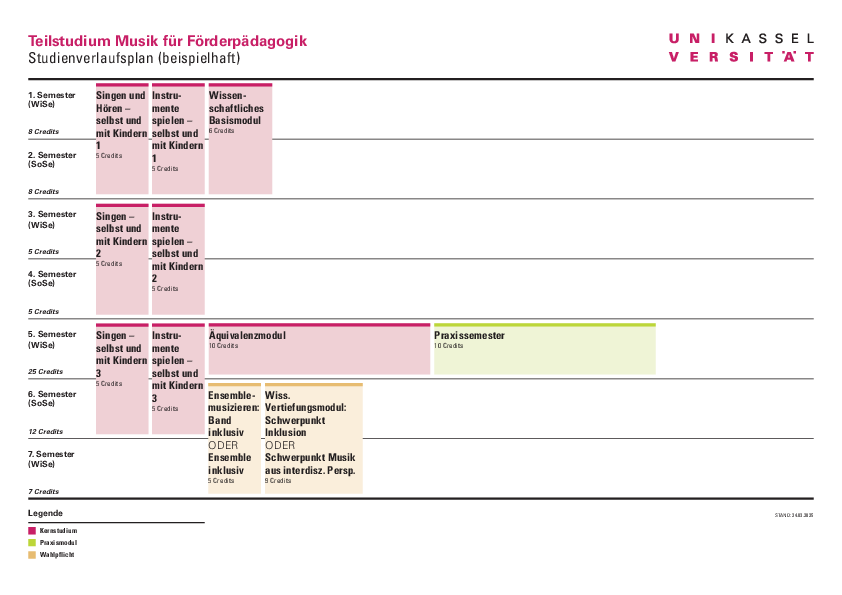
Sample study plan
Download
- Sample curriculum for the Music Elementary School program - PDF 79 KB
- Sample curriculum for the Music Secondary and Middle School program - PDF 77 KB
- Sample curriculum for the Music Secondary School sub-degree program - PDF 83 KB
- Sample curriculum for the Music Special Education degree program - PDF 83 KB