Orientation phase
The content on this page was translated automatically.
The one-year orientation phase is divided into two areas: STEM Orientation and the STEM Accompanying Program.
In the STEM orientation section, you will attend at least one mathematics course, one or more practical STEM projects, specialist courses from the various study specializations and key skills courses. To complete the module, you must complete coursework and/or examinations in each of these courses. The total amount of coursework to be completed in this area is 30 credits for the entire orientation year.
In the STEM accompanying program, you will attend a plusMINT lecture series, various mentoring offers, the plusMINT seminar, preliminary and bridging courses and you can get a taste of any specialist courses without any obligation. No examinations are taken in the MINT accompanying program and no credits are earned. Active participation in these courses is recorded via academic achievements or course transcripts and recorded in the form of semester hours per week (SWS). The total number of courses to be taken in this area for the entire orientation year is 20 SWS.
More details on the individual courses can be found below.
In both areas, there are compulsory courses that you must attend and compulsory elective courses from which you can choose the ones that suit you best:
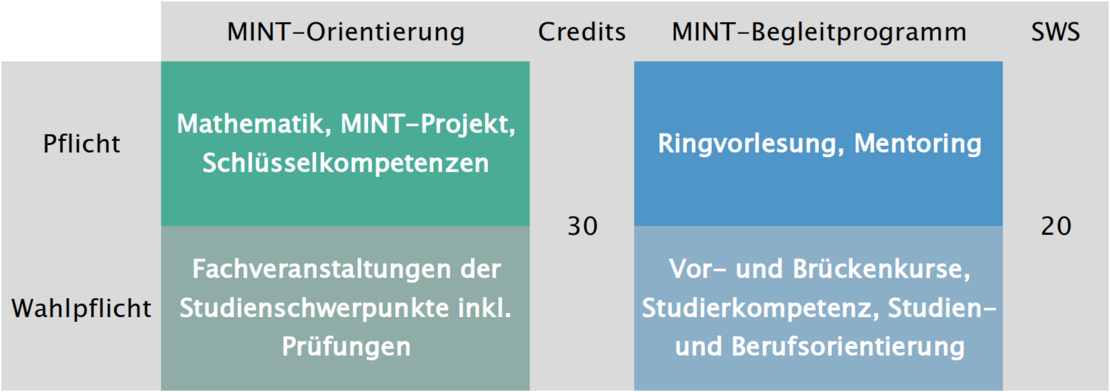
Range of events:
SWS stands for semester hours per week, WiSe for winter semester, SoSe for summer semester.
Compulsory courses MINT orientation
These courses must be attended.
Only one of the following courses must be taken. If the introductory mathematics test is not passed, the "Advanced Mathematics Course" must be taken. Otherwise, "Mathematics I" or "Introduction to Analysis I" or "Fundamentals of Mathematics" + "Elementary Linear Algebra" can also be taken.
Advanced course in mathematics
The aim of the advanced course with 6 credits (2 SWS lecture incl. exercise in the winter semester + 2 SWS lecture incl. exercise in the summer semester) is to bring students' mathematical knowledge and skills up to the mathematical advanced level, which may not have been reached before. In addition, the targeted treatment of further fundamental content from the mathematical courses of the specializations ensures a barrier-free introduction to the mathematical modules of the specializations. The advanced mathematics course is based on the mathematical content taught in Hessian grammar schools at advanced course level and other fundamental content from the mathematics courses: Number ranges, fraction terms, power laws, elementary functions, differential and integral calculus and basic concepts of linear algebra. No prerequisites.
Mathematics I
This module with 9 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in the winter semester) corresponds to the basic mathematics course in the first semester of the engineering degree courses. The course content includes vector calculus in the plane and in space, sequences and series of real numbers, real functions of a variable and differential and integral calculus of a variable. A mandatory prerequisite for participation in the exam is passing the mathematics entrance test.
Introduction to Analysis I
This module with 10 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in the winter semester) corresponds to the basic analysis course in the first semester of the Mathematics, Technomathematics and Physics degree programs. Content is an in-depth introduction to basic structures and methods of analysis: metric spaces, convergence, continuity, structure of the real number system, basic properties of complex numbers, sequences, series in R and in C, differential calculus and integral calculus with one variable. A mandatory prerequisite for participation in the exam is passing the mathematics entrance test.
Fundamentals of Mathematics + Elementary Linear Algebra
These two modules with 5 credits each (2 SWS lecture + 1 SWS exercise in winter semester) correspond to the basic mathematics courses in the first semester of Mathematics and Technomathematics. The contents of "Fundamentals of Mathematics" are the introduction to the mathematical formula language, elementary set theory and logic, mathematical problem solving and mathematical proof. The content of "Elementary Linear Algebra" includes solving linear systems of equations, real vector spaces and linear mappings, calculating with vectors and matrices, calculating determinants, eigenvalues and eigenvectors. A mandatory prerequisite for participation in the exam is passing the mathematics entrance test.
STEM projects are offered at all participating faculties, one of which must be chosen as a compulsory project. If desired, additional STEM projects can be taken as elective projects. The STEM projects provide an introduction to project work and are completed with an academic achievement. They include practical components which, depending on the project task, can consist of your own experiments, modeling or construction tasks, for example. Through your own practical work in teams, you will gain insights into the methods, objects of investigation and application perspectives of the respective subject and get to know its specific specialist culture.
The topics of the STEM projects offered vary. Examples of regularly offered STEM projects are
- STEM project nanostructure science"Nanostructures in everyday life":
Experiments on sunscreen, coated surfaces, natural dyes and much more in the chemistry lab. - STEM physics project"Spectroscopy and greenhouse gases":
Experiments with lasers, light, colors and absorption of greenhouse gases, etc. on research equipment. - STEM civil engineering project"Tensegrity - design, mathematics, mechanics and application of tense structures":
Theory and experiments on interesting constructions made of rods and ropes. - STEM project Mathematics/Technomathematics"Mathematical Modeling":
Introduction to mathematical modeling and simulation as a basis for all STEM subjects using illustrative examples. - STEM projects in mechanical engineering:
From water rockets to smart coffee machines to programming humanoid robots, you can choose from a variety of student projects. You can find more detailed information here.
You can find out which STEM projects are offered in the respective semester via a Moodle course.
You can take courses from the university-wide catalog for additive key competencies: For example, various language courses, methodology workshops and seminars on the environment and sustainability.
Compulsory courses MINT accompanying program
These courses must be attended.
In the lecture series, the available study specializations are presented in detail. Lecturers explain the respective course structure and provide insights into interesting areas of research. This university-internal overview of the specializations is supplemented by presentations from external guests from various companies in the STEM sector. They provide practical information about possible career fields and give an insight into their activities and working methods. After the presentations, you can talk to all the speakers in an informal atmosphere. By attending the lecture series, you will gain an interdisciplinary overview of the orientations and career prospects of all the specializations offered and will be supported in making an informed choice of specialization after the orientation phase.
The lecture series comprises 3 SWS per semester. Coursework is completed in the form of lecture notes.
The topics on the individual dates of the lecture series are published in a corresponding Moodle course.
One of the main components of the orientation phase is the diverse and intensive personal advice and support provided to students to promote successful studies. This is primarily realized through a three-stage mentoring program and a weekly seminar in which interdisciplinary skills are learned for the further course of studies.
The mentoring consists of three levels of support: Student buddies from previous cohorts provide an introduction to everyday life at the university in the first semester and give tips for a successful start to your studies; Professors provide support in a group and one-to-one discussion on choosing a major; plusMINT project members provide advice and offer at least 2x2 SWS seminar in the winter and summer semesters.
In addition to counseling opportunities, especially for the orientation phase, the plusMINT seminar offers workshops and lectures that are primarily intended to strengthen interdisciplinary study skills: Choosing a course of study, study and examination organization, IT skills, opportunities for student engagement as well as gender and diversity.
Participation in 1 SWS of mentoring per semester must be proven. Coursework is achieved through attendance and written reflection tasks.
The topics of the individual plusMINT seminar dates are published in a corresponding Moodle course.
Compulsory elective courses MINT orientation
You can choose freely from the following courses in the orientation phase, whereby you must take 14-18 credits depending on the mathematics course you choose.
Mechanics I
This compulsory module for civil and environmental engineering consists of the course of the same name (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS tutorial + 2 SWS tutorial) and is offered in the winter semester. The 6C module is completed with a written exam (60 min.). In this course, the basic methodology of mechanics is taught, taking into account the aspects of modeling and analysis. For example, students will be able to create mechanical models of simple technical systems, calculate centers of gravity of bodies or determine the equilibrium of structures. Participation in the Mathematics I module is recommended.
Materials in civil engineering I
This compulsory module for civil and environmental engineering consists of the course of the same name (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise) and is offered across semesters starting in the winter semester. The 6C module is completed with a written exam (90 min.) in the summer semester. Mechanical and building physics fundamentals for the assessment of materials and their behavior in use as well as the basics of standards, production and behavior of e.g. cement, gypsum, lime, concrete, mortar and building ceramics etc. are taught. No prerequisites.
Building Construction I / Representation Technology
This compulsory module for civil engineering consists of the courses "Building Construction I" (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS tutorial) and "Representation Technology / CAD" (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS tutorial + compact course/practical) and both take place in the winter semester. The 5C module is completed with a written exam (45 min.) in Building Construction I. Students will learn about the functionality of buildings and construction elements, building typology, the basics of structural drawing, the use of practice-oriented programs and the graphical representation of three-dimensional objects. No prerequisites.
Building Construction II / Building Physics
This compulsory module for civil engineering combines the courses "Structural Design II" (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS tutorial) and "Building Physics" (2 SWS lecture), both of which take place in the summer semester. The 5C module is completed with two written examinations (45 & 60 min.). Knowledge of loads and load flow, masonry construction and building physics basics, e.g. effects of cold, heat, moisture and noise are taught. Completion of the module Building Construction I / Representation Technology is recommended.
Surveying
This compulsory module for civil and environmental engineering consists of the course "Surveying" (4 SWS lecture + exercises in small groups) and takes place in the summer semester. The 6C module is completed with a written exam (120 min.) The course contents are the basic procedures for the realization of the spatial reference (georeferencing) and the spatial data acquisition. This includes, for example, units of measurement, measurement accuracy, coordinate systems, instrumentation and the production of site and elevation plans. No prerequisites.
Fundamentals of construction management and construction operations I
This compulsory (Civil Engineering) or compulsory elective module (Environmental Engineering) consists of the course "Fundamentals of Construction Management and Construction Operations I" (4 SWS lecture + office hours) and takes place in the summer semester. The 6C module is completed with a written exam (120 min.). Students learn the basics of construction project planning through to acceptance. This includes an understanding of (construction) companies in the economic and legal system, the basics of contract law as well as cost accounting systems and the calculation of construction services and fees. No prerequisites.
Transport basics
This compulsory module for civil and environmental engineering consists of the courses Fundamentals of Transport Planning (2 SWS lecture + tutorial) and Fundamentals of Transport Engineering (2 SWS + repeat tutorial/meeting), both of which take place in the summer semester. The 6C module is completed with a combined examination (120 min.). Knowledge and methods of the essential planning steps are taught, e.g. for the survey and forecast of traffic demand or for network design. In addition, students should understand traffic engineering systems and be able to carry out relevant calculations. No prerequisites.
Mathematics 2
Compulsory module in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Civil Engineering and Environmental Engineering, compulsory elective module in the Bachelor of Nanostructure Sciences with 9 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in the summer semester). Course contents are mainly linear systems of equations, matrices, differential and integral calculus of several variables and differential equations. Recommended prerequisite is attendance of "Mathematics I".
The module descriptions are excerpts from the module handbook for the Bachelor of Civil Engineering course. This and further information can be found on the course homepage.
Digital Logic
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Electrical Engineering with 4 credits (2 SWS lecture + 1 SWS exercise in the winter semester), compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Computer Science. Course content includes number representation and codes, Boolean algebra, design and simplification of switching networks, analysis and synthesis of switching systems, control unit design and microprogram control. No prerequisites.
Fundamentals of electrical engineering 1
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Electrical Engineering and Mechatronics with 11 credits consisting of the courses "Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering 1" (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS practical in winter semester) and "Electrotechnical Practical 1" (2 SWS laboratory practical in winter semester). Course content includes the calculation of currents and voltages in electrical networks, electrostatic fields and stationary electrical flow fields. Mastery of elementary analysis and vector algebra is recommended.
Introduction to programming
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Electrical Engineering and Mechatronics (2 SWS lecture + 1 SWS exercise in winter semester). The basics of imperative programming are taught. No prerequisites.
Fundamentals of electrical engineering 2
Compulsory module in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Electrical Engineering and Mechatronics with 9 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in the summer semester). Course contents are stationary and time-varying magnetic fields, alternating current theory and conductors. Recommended prerequisites are mastery of elementary analysis, vector algebra and complex calculus. Recommended prerequisites are the module "Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering 1" and an understanding of infinite series and complex calculus.
Object-oriented programming + programming project
Compulsory module in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Mechatronics and Electrical Engineering with 6 credits (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS practical course in the summer semester). Teaching content is object-oriented programming.
Computer Architecture
This compulsory module for computer science and electrical engineering consists of the course of the same name (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS practical) and takes place in the summer semester. This 6C module is completed with a written exam (90-120 min.). Course contents are the basics of information representation in computer systems as well as coding, automata and evaluation criteria of computer architectures. Students learn about the structure of different architectures and their characteristics. Recommended prerequisites are the modules "Technical Foundations of Computer Science", "Introduction to Computer Science" and "Fundamentals of Mathematics" or programming knowledge and the module "Digital Logic".
The module descriptions are excerpts from the module handbook for the Bachelor of Electrical Engineering degree program. This and further information can be found on the course homepage.
Introduction to Computer Science
This compulsory module for the Bachelor of Computer Science, Mathematics and Technomathematics consists of the course of the same name (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise) and takes place in the winter semester. This 9C module is completed with a written exam (90-120 min.). Students acquire skills in the development of imperative procedural programs as well as object-oriented programming in Java and elementary knowledge of another programming language. In addition, they learn basic concepts of computer science related to programming. No prerequisites.
Technical foundations of computer science
This compulsory module in the first semester of Computer Science consists of the sub-modules/events "Electrical Engineering for Computer Scientists" (2 SWS lecture + 1 SWS tutorial + 2 SWS tutorial in the winter semester) and "Digital Logic" (2 SWS lecture + 1 SWS tutorial in the winter semester). The content of "Electrical Engineering for Computer Scientists" includes basic physical and technical relationships in the field of electrical engineering as well as applications of methods for calculating DC networks. The content of "Digital Logic" includes number representation and codes, Boolean algebra, design and simplification of switching networks, analysis and synthesis of switching systems, control unit design and microprogram control. Recommended prerequisites for "Electrical Engineering for Computer Scientists" are a good knowledge of upper-level mathematics (basic concepts of differential and integral calculus and algebra).
Algorithms and data structures
This compulsory module for the Bachelor of Computer Science and Technomathematics or compulsory elective module for the Bachelor of Electrical Engineering consists of the course of the same name (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise) and takes place in the summer semester. The 6C module is completed with a written exam (75-120 min.). Elementary knowledge of algorithms and data structures in computer science as well as skills in understanding and developing algorithms are taught. The module "Introduction to Computer Science" or "Introduction to Programming" is recommended.
Computer Architecture
This compulsory module for computer science and electrical engineering consists of the course of the same name (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise) and takes place in the summer semester. This 6C module is completed with a written exam (90-120 min.). Course contents are the basics of information representation in computer systems as well as coding, automata and evaluation criteria of computer architectures. Students learn about the structure of different architectures and their characteristics. Recommended prerequisites are the modules "Technical Foundations of Computer Science", "Introduction to Computer Science" and "Fundamentals of Mathematics" or programming knowledge and the module "Digital Logic".
Laboratory C/Embedded Systems
This compulsory module for Computer Science consists of the course "Laboratory C" (2 SWS lecture) and a practical course "Laboratory Embedded Systems" (2 SWS practical course) and takes place in the summer semester. The 6C module is completed with a written exam (Laboratory C) and a practical report (Laboratory Embedded Systems). Students acquire the ability to create hardware-related programs in the C programming language and apply this in practice. Recommended prerequisites are the modules "Introduction to Computer Science" and "Technical Foundations of Computer Science". In addition, passing the exam for "Laboratory C" is mandatory for participation in the practical part "Laboratory Embedded Systems".
Learning and organization
This compulsory module for Computer Science consists of the course of the same name (1 SWS lecture) and takes place in the winter semester. The 2C module is completed with a written assignment relating to the content of another computer science course. This module is intended to support students in successfully completing their studies by teaching self-management techniques such as planning, time management and targeted exam preparation as well as the ability to reflect and deal resiliently with failure. No prerequisites.
The module descriptions are excerpts from the module handbook of the Bachelor of Computer Science degree program. This and further information can be found on the course homepage.
CAD - Computer Aided Design
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering and Mechatronics with 6 credits (2 SWS lecture + 4 SWS exercise in winter semester). Course content includes the basics of technical drawing (including standard fonts, dimensioning, representation of standard parts, sections, computer-aided CAD design). No prerequisites.
Sustainability, resource utilization and product life cycles
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering and Mechatronics with 4 credits (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in winter semester). Course content includes environmental accounting, material cycles and technology assessment. No prerequisites.
Introduction to mechanical engineering
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering and Mechatronics with 3 credits (2 SWS lecture series + 2 SWS seminar in the winter semester). The lecture series presents work and research topics in mechanical engineering and mechatronics, the seminar deals with self-organization and time management. No prerequisites.
Computer science: basics of programming
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering with 6 credits (2 SWS lecture + 3 SWS exercise in winter semester). Course content includes principles, methods, concepts and notations of programming (simple data structures, object orientation, etc.). Knowledge of computer applications is recommended.
Materials engineering
Compulsory module in the 1st and 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering with 8 credits consisting of the courses "Materials Engineering 1" (2 SWS lecture + 1 SWS exercise in the winter semester), "Materials Engineering 2" (2 SWS lecture + 1 SWS exercise in the summer semester) and the "Materials Engineering Practical" (2 SWS as a block). Course contents are mainly the structural composition of construction materials (especially various iron and aluminum materials) and the behavior under mechanical stress. No prerequisites.
Electrical engineering and electronics in mechanical engineering
Compulsory module in the 3rd semester of the Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering with 6 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in winter semester). Course content includes direct current networks, measurement methods, alternating current theory, semiconductor components (diodes, transistors), basic transistor circuits. Recommended prerequisites are basic knowledge of analysis and vector algebra.
Design engineering 1
Compulsory module in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering and in the 4th semester of the Bachelor of Mechatronics with 6 credits (2 SWS lecture + 4 SWS exercise in the summer semester). Course content includes the design of screws, springs and rivets, design of welding, soldering, bonding, 3D design techniques. Recommended prerequisites are the modules "CAD" and "Mathematics 1".
Production engineering 1
Compulsory module in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering with 3 credits (2 SWS lecture in the summer semester). Course content includes the basics of cutting manufacturing processes (drilling, turning, milling, grinding, water jet cutting, laser cutting, etc.). No prerequisites.
Technical Mechanics 1
Compulsory module in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering, compulsory elective module in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Mechatronics with 6 credits (3 SWS lecture + 3 SWS exercise in the summer semester). Course content includes statics (including force systems, center of gravity, internal forces) and the kinetics of the center of mass (including momentum and energy theorem, vibrations). Knowledge of mathematics at A-level is recommended.
Chemistry for engineers
Compulsory elective module of the Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering with 2 credits (2 SWS lecture in winter semester). Course content is basic knowledge of chemistry (including the structure of matter, chemical reactions, electrochemistry and organic chemistry). No prerequisites.
The module descriptions are excerpts from the module handbook for the Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering degree program. This and further information can be found on the course homepage.
Fundamentals of Mathematics
This module with 5 credits (2 SWS lecture + 1 SWS exercise in the winter semester) corresponds to the compulsory course in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Mathematics and Technomathematics. The course content includes an introduction to mathematical formula language, elementary set theory and logic, mathematical problem solving and mathematical proof. A mandatory prerequisite for participation in the examination is passing the mathematics entrance test.
Elementary linear algebra
This module with 5 credits (2 SWS lecture + 1 SWS exercise in the winter semester) corresponds to the compulsory course in the 1st semester of the Bachelor's degree in Mathematics, Technomathematics and Physics. Course content includes solving linear systems of equations, real vector spaces and linear mappings, calculating with vectors and matrices, calculating determinants, eigenvalues and eigenvectors. A mandatory prerequisite for participation in the exam is passing the mathematics entrance test.
Introduction to Analysis I
This module with 10 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in the winter semester) corresponds to the basic analysis course in the first semester of the Mathematics, Technomathematics and Physics degree programs. Content is an in-depth introduction to basic structures and methods of analysis: metric spaces, convergence, continuity, structure of the real number system, basic properties of complex numbers, sequences, series in R and in C, differential calculus and integral calculus with one variable. A mandatory prerequisite for participation in the exam is passing the mathematics entrance test.
Introduction to Analysis II
Compulsory course in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Mathematics, Technomathematics and Physics with 10 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in the summer semester). Course content is the mathematically detailed treatment of analysis with several variables (including curve integrals, extrema with constraints, gradient fields). It is recommended that students attend "Analysis I" and "Elementary Linear Algebra".
Linear algebra and analytic geometry
Compulsory course in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Mathematics, Technomathematics and Physics with 10 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in the summer semester). Course content is the mathematically detailed treatment of linear algebra and analytic geometry (including abstract vector spaces and linear mappings, matrix normal forms, Euclidean vector spaces, affine spaces, scalar product). No prerequisites.
Introduction to computer science
This compulsory module for the Bachelor of Computer Science, Mathematics and Technomathematics consists of the course of the same name (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise) and takes place in the winter semester. This 9C module is completed with a written exam (90-120 min.). Students acquire skills in the development of imperative procedural programs as well as object-oriented programming in Java and elementary knowledge of another programming language. In addition, they learn basic concepts of computer science related to programming. No prerequisites.
Further information can be found on the course homepage.
CAD - Computer Aided Design
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering and Mechatronics with 6 credits (2 SWS lecture + 4 SWS exercise in winter semester). Course content includes the basics of technical drawing (including standard fonts, dimensioning, representation of standard parts, sections, computer-aided CAD design). No prerequisites.
Fundamentals of electrical engineering 1
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Mechatronics and Electrical Engineering with 11 credits consisting of the courses "Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering 1" (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS practical course in winter semester) and "Electrotechnical practical course 1" (2 SWS laboratory practical course in winter semester). Course content includes the calculation of currents and voltages in electrical networks, electrostatic fields and stationary electrical flow fields. Mastery of elementary analysis and vector algebra is recommended.
Sustainability, resource utilization and product life cycles
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering and Mechatronics with 4 credits (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in winter semester). Course content includes environmental accounting, material cycles and technology assessment. No prerequisites.
Introduction to mechatronics
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering and Mechatronics with 3 credits (2 SWS lecture series + 2 SWS seminar in winter semester). The lecture series presents work and research topics in mechanical engineering and mechatronics, the seminar deals with self-organization and time management. No prerequisites.
Introduction to programming
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Electrical Engineering and Mechatronics (2 SWS lecture + 1 SWS exercise in winter semester). The basics of imperative programming are taught. No prerequisites.
Design engineering 1
Compulsory module in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering and in the 4th semester of the Bachelor of Mechatronics with 6 credits (2 SWS lecture + 4 SWS exercise in the summer semester). Course content includes the design of screws, springs and rivets, design of welding, soldering, bonding, 3D design techniques. Recommended prerequisites are the modules "CAD" and "Mathematics 1".
Fundamentals of electrical engineering 2
Compulsory module in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Electrical Engineering and Mechatronics with 9 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in the summer semester). Course contents are stationary and time-varying magnetic fields, alternating current theory and conductors. Recommended prerequisites are mastery of elementary analysis, vector algebra and complex calculus. Recommended prerequisites are the module "Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering 1" and an understanding of infinite series and complex calculus.
Object-oriented programming + programming project
Compulsory module in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Mechatronics and Electrical Engineering with 6 credits (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS practical course in the summer semester). Teaching content is object-oriented programming.
Materials of mechanical engineering
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Mechatronics with 3 credits (2 SWS lecture in the summer semester). Course contents are the structural and physical properties of metallic materials, ceramics and plastics. No prerequisites.
Technical Mechanics 1
Compulsory module in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Mechanical Engineering, compulsory elective module in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Mechatronics with 6 credits (3 SWS lecture + 3 SWS exercise in the summer semester). Course content includes statics (including force systems, center of gravity, internal forces) and the kinetics of the center of mass (including momentum and energy theorem, vibrations). Knowledge of mathematics at A-level is recommended.
The module descriptions are excerpts from the module handbook of the Bachelor of Mechatronics degree program. This and further information can be found on the course homepage.
Introduction to nanostructure sciences
Compulsory module in the 1st year of the Bachelor of Nanostructure Sciences with 9 credits consisting of the lecture series "Introduction to Nanostructure Sciences" (2 SWS in the winter semester) and "Fundamentals of Biology for Nanostructure Sciences" (2 SWS in the winter semester) as well as the lecture seminar "Introduction to Nanostructure Sciences" (2 SWS in the summer semester) and the laboratory practical course "Basic Physical-Biophysical Practical Course" (3 SWS in the summer semester). Course content includes the basics of nanostructures, fields of application of nanotechnology and basic measurement experiments. No prerequisites.
Mechanics and Heat / Experimental Physics I
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Physics with 7 credits and the Bachelor of Nanostructure Sciences with 9 credits (5 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in winter semester). Course content includes detailed treatment of Newtonian mechanics (including motion, force fields, oscillations) and thermodynamics (including kinetic gas theory, laws of thermodynamics, heat transport). No prerequisites.
General chemistry
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Nanostructure Sciences with 7 credits consisting of a lecture (3 SWS in the winter semester), an exercise (1 SWS in the winter semester), a seminar (1 SWS in the winter semester) and a practical course (2 SWS in the winter semester). Course content includes chemical bonding, kinetics and chemical equilibrium, acids and bases, oxidation and reduction. No prerequisites.
Mathematical methods of physics (I)
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Physics with 6 credits and the Bachelor of Nanostructure Sciences with 8 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in winter semester). Course content is important mathematical tools for application in the natural sciences such as vector algebra, Taylor expansion, partial derivatives and multiple integrals, simple differential equations, scalar and vector fields. No prerequisites.
Literature research
Elective module in the Bachelor of Nanostructure Sciences with 2 credits (2 SWS lecture incl. exercise in winter semester). Course content includes scientific citation methods, IT-supported creation of bibliographies, overview of the relevant specialist journals and literature databases in nanostructure sciences, physics, biology and chemistry. No prerequisites.
Electricity and Optics / Experimental Physics II
Compulsory module in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Physics with 7 credits and the Bachelor of Nanostructure Sciences with 9 credits (5 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in the summer semester). Course content includes detailed treatment of electrostatics (e.g. charge, electric potential), electrodynamics (e.g. electric current, magnetic fields, induction, Maxwell's equations, electromagnetic waves) and optics (e.g. electromagnetic waves in matter, refraction, interference, diffraction, optical instruments). Good school knowledge of mathematics is recommended.
Mathematical methods of physics II
Compulsory module in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Nanostructure Sciences with 5 credits (2 SWS lecture + 1 SWS exercise in the summer semester). The course content is important mathematical tools for application in the natural sciences such as integral theorems of Gauss and Stokes, curved coordinate systems, Fourier series and integrals, Fourier and Laplace transformations, probability distribution, statistics, error calculation, functions of complex variables. The module "Mathematical Methods of Physics I" is a mandatory prerequisite.
The module descriptions are excerpts from the module handbook for the Bachelor of Nanostructure Sciences degree program. This and further information can be found on the course homepage.
Experimental Physics I / Mechanics and Heat
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Physics with 7 credits and the Bachelor of Nanostructure Sciences with 9 credits (5 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in winter semester). Course content includes detailed treatment of Newtonian mechanics (including motion, force fields, oscillations) and thermodynamics (including kinetic gas theory, laws of thermodynamics, heat transport). No prerequisites.
Mathematical methods of physics (I)
Compulsory module in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Physics with 6 credits and the Bachelor of Nanostructure Sciences with 8 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in winter semester). Course content is important mathematical tools for application in the natural sciences such as vector algebra, Taylor expansion, partial derivatives and multiple integrals, simple differential equations, scalar and vector fields. No prerequisites.
General Chemistry
Compulsory module in the 3rd semester of the Bachelor of Physics with 7 credits consisting of a lecture (3 SWS in the winter semester), an exercise (1 SWS in the winter semester) and a practical laboratory course (3 SWS in the winter semester). Course content includes chemical bonding, kinetics and chemical equilibrium, acids and bases, oxidation and reduction. No prerequisites.
Experimental Physics II / Electricity and Optics
Compulsory module in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Physics with 7 credits and the Bachelor of Nanostructure Sciences with 9 credits (5 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in the summer semester). The course content includes a detailed treatment of electrostatics (e.g. charge, electric potential), electrodynamics (e.g. electric current, magnetic fields, induction, Maxwell's equations, electromagnetic waves) and optics (e.g. electromagnetic waves in matter, refraction, interference, diffraction, optical instruments). The modules Mathematical Methods of Physics, Experimental Physics I and Analysis I are recommended prerequisites.
Introduction to Analysis II
Compulsory course in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Mathematics, Technomathematics and Physics with 10 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in the summer semester). Course content is the mathematically detailed treatment of analysis with several variables (including curve integrals, extrema with constraints, gradient fields). It is recommended that students attend "Analysis I" and "Elementary Linear Algebra".
Linear algebra and analytic geometry
Compulsory course in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Mathematics, Technomathematics and Physics with 10 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in the summer semester). Course content is the mathematically detailed treatment of linear algebra and analytic geometry (including abstract vector spaces and linear mappings, matrix normal forms, Euclidean vector spaces, affine spaces, scalar product). No prerequisites.
The module descriptions are excerpts from the module handbook for the Bachelor's degree course in Physics. This and further information can be found on the course homepage.
Fundamentals of Mathematics
This module with 5 credits (2 SWS lecture + 1 SWS exercise in the winter semester) corresponds to the compulsory course in the 1st semester of the Bachelor of Mathematics and Technomathematics. The course content includes an introduction to mathematical formula language, elementary set theory and logic, mathematical problem solving and mathematical proof. A mandatory prerequisite for participation in the examination is passing the mathematics entrance test.
Elementary linear algebra
This module with 5 credits (2 SWS lecture + 1 SWS exercise in the winter semester) corresponds to the compulsory course in the 1st semester of the Bachelor's degree in Mathematics, Technomathematics and Physics. Course content includes solving linear systems of equations, real vector spaces and linear mappings, calculating with vectors and matrices, calculating determinants, eigenvalues and eigenvectors. A mandatory prerequisite for participation in the exam is passing the mathematics entrance test.
Introduction to Analysis I
This module with 10 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in the winter semester) corresponds to the basic analysis course in the first semester of the Mathematics, Technomathematics and Physics degree programs. Content is an in-depth introduction to basic structures and methods of analysis: metric spaces, convergence, continuity, structure of the real number system, basic properties of complex numbers, sequences, series in R and in C, differential calculus and integral calculus with one variable. A mandatory prerequisite for participation in the exam is passing the mathematics entrance test.
Introduction to computer science
This compulsory module for the Bachelor of Computer Science, Mathematics and Technomathematics consists of the course of the same name (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise) and takes place in the winter semester. This 9C module is completed with a written exam (90-120 min.). Students acquire skills in the development of imperative procedural programs as well as object-oriented programming in Java and elementary knowledge of another programming language. In addition, they learn basic concepts of computer science related to programming. No prerequisites.
Introduction to Analysis II
Compulsory course in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Mathematics, Technomathematics and Physics with 10 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in the summer semester). Course content is the mathematically detailed treatment of analysis with several variables (including curve integrals, extrema with constraints, gradient fields). It is recommended that students attend "Analysis I" and "Elementary Linear Algebra".
Linear algebra and analytic geometry
Compulsory course in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Mathematics, Technomathematics and Physics with 10 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in the summer semester). Course content is the mathematically detailed treatment of linear algebra and analytic geometry (including abstract vector spaces and linear mappings, matrix normal forms, Euclidean vector spaces, affine
spaces, scalar product). No prerequisites.
Algorithms and data structures
This compulsory module for the Bachelor of Computer Science and Technomathematics or compulsory elective module for the Bachelor of Electrical Engineering consists of the course of the same name (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise) and takes place in the summer semester. The 6C module is completed with a written exam (75-120 min.). Elementary knowledge of algorithms and data structures in computer science as well as skills in understanding and developing algorithms are taught. The module "Introduction to Computer Science" or "Introduction to Programming" is recommended.
Further information can be found on the course homepage.
Mechanics I
This compulsory module for civil and environmental engineering consists of the course of the same name (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS tutorial + 2 SWS tutorial) and is offered in the winter semester. The 6C module is completed with a written exam (60 min.). In this course, the basic methodology of mechanics is taught, taking into account the aspects of modeling and analysis. For example, students will be able to create mechanical models of simple technical systems, calculate centers of gravity of bodies or determine the equilibrium of structures. Participation in the Mathematics I module is recommended.
Materials in civil engineering
This compulsory module for civil and environmental engineering consists of the course of the same name (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise) and is offered across semesters starting in the winter semester. The 6C module is completed with a written exam (90 min.) in the summer semester. Mechanical and building physics fundamentals for the assessment of materials and their behavior in use as well as the basics of standards, production and behavior of e.g. cement, gypsum, lime, concrete, mortar and building ceramics etc. are taught. No prerequisites.
Fundamentals of environmental science 1
This compulsory module for environmental engineering consists of the courses "Environmental Science Fundamentals for Engineers" (2 SWS lecture) in the winter semester and "Modeling and Simulation" (2 SWS seminar) in the summer semester. The 6C module is completed with a written exam in the summer semester (90 min.). In the three subject areas of land use and ecosystems, climate and water, students learn, for example, the basics of soil science, the effects of anthropogenic climate change and the hydrological cycle. In addition, in the subject areas of system analysis and water management systems, e.g. modeling and evaluation, dynamic modeling as well as models and methods for system planning are taught. Basic knowledge of environmental sciences is recommended.
Building Construction / Building Physics / Representation Technology
This compulsory module for Environmental Engineering consists of the three courses "Building Construction I" (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS tutorial), "Building Physics" (2 SWS lecture) and "Representation Technology / CAD" (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS tutorial + compact course/practical). Building Construction I and Representation Technology / CAD take place in the winter semester, Building Physics in the summer semester. The 7C module is completed with two written examinations in Building Construction I and Building Physics (45 & 60 min.). Knowledge of the functionality of buildings and construction elements, building typology, the basics of construction drawing, the application of practice-oriented programs and the graphic representation of three-dimensional bodies as well as building physics basics, e.g. effects of cold, heat, moisture and noise are taught. No prerequisites.
Hydrology and hydrogeology
This compulsory elective module for environmental engineering consists of the course of the same name (2 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise) and takes place in the summer semester. The 6C module is completed with a written exam (120 min.). Students should become familiar with the various characteristics of the elements of the hydrological cycle, evaluate them mathematically and record them using measurement technology. No prerequisites.
Fundamentals of environmental science 2
This compulsory module for environmental engineering consists of the courses Environmental Chemistry (2 SWS lecture + tutorial) and Ecology (2 SWS lecture + tutorial), both of which take place in the summer semester. The module is completed with a written exam (120-180 min.). The basics of general and toxicology, selected environmental pollution and environmental analysis as well as elementary ecological processes and knowledge about e.g. organisms, populations, ecosystems as well as biodiversity and nature conservation are taught. Basic knowledge of physics, chemistry, mathematics and environmental science is recommended.
Transport basics
This compulsory module for civil and environmental engineering consists of the courses Fundamentals of Transport Planning (2 SWS lecture + tutorial) and Fundamentals of Transport Engineering (2 SWS + repeat tutorial/lecture), both of which take place in the summer semester. The 6C module is completed with a combined examination (120 min.). Knowledge and methods of the essential planning steps are taught, e.g. for the survey and forecast of traffic demand or for network design. In addition, students should understand traffic engineering systems and be able to carry out relevant calculations. No prerequisites.
Resource management and waste technology
This compulsory module for Environmental Engineering consists of the three courses "Fundamentals of Waste Technology" (2 SWS lecture), "Resource and Waste Management" (2 SWS lecture) and "Mechanical Waste Processing and Recycling" (2 SWS lecture). While the fundamentals of waste technology takes place in the summer semester, the other two courses are offered in the winter semester. The 9C module is completed with three written examinations (60 minutes each). The course content includes scientific and technical principles of waste management processes and central waste streams, including waste treatment technologies, as well as legal and economic aspects and material recovery processes for various types of waste. No prerequisites.
Surveying
This compulsory module for civil and environmental engineering consists of the course "Surveying" (2 SWS lecture + exercises in small groups) and takes place in the summer semester. The 6C module is completed with a written exam (120 min.) The course contents are the basic procedures for the realization of the spatial reference (georeferencing) and the spatial data acquisition. This includes, for example, units of measurement, measurement accuracy, coordinate systems, instrumentation and the production of site and elevation plans. No prerequisites.
Mathematics 2
Compulsory module in the 2nd semester of the Bachelor of Civil Engineering and Environmental Engineering, compulsory elective module in the Bachelor of Nanostructure Sciences with 9 credits (4 SWS lecture + 2 SWS exercise in the summer semester). Course contents are mainly linear systems of equations, matrices, differential and integral calculus of several variables and differential equations. Recommended prerequisite is attendance of "Mathematics I".
The module descriptions are excerpts from the module handbook of the Bachelor of Environmental Engineering degree program. This and further information can be found on the course homepage.
STEM projects are offered at all participating faculties, one of which must be chosen as a compulsory project. If desired, additional STEM projects can be taken as elective projects. Further information on the STEM projects can be found here.
Compulsory elective courses MINT accompanying program
You can choose freely from the following courses in the orientation phase, whereby you must take 12 semester hours per week (SWS).
In addition to the mandatory 1 semester hour of mentoring per semester (see above), students can also attend other plusMINT seminars in which they can learn interdisciplinary skills for the rest of their studies.
In addition to counseling opportunities, especially for the orientation phase, the plusMINT seminar offers workshops and lectures that are primarily intended to strengthen interdisciplinary study skills: Choosing a course of study, organizing studies and examinations, IT skills, opportunities for student engagement as well as gender and diversity.
The topics of the individual plusMINT seminar dates are published in a corresponding Moodle course.
You can attend all of the university's STEM courses without having to take an exam.
This gives you an insight into the courses that you may have to expect in your future major and allows you to familiarize yourself with the topics covered there without pressure, so that you will have fewer problems in your major later in the course and examination. You can also get to know the different perspectives and working methods of different disciplines without the pressure of exams.
A learning log must be created for each double lesson attended, in which you reflect on what you have learned and any difficulties you have encountered, or (if this is not used later for the completion of a module) the academic achievement of the course must be fulfilled.
You can also attend all of the university's STEM courses on an irregular basis without having to take an exam.
This gives you an insight into the courses you can expect to attend in your future major. These can be taster visits to courses from higher semesters. On the other hand, you will get to know the different perspectives and working methods of different disciplines at an early stage.
A learning log must be created for each double lesson attended, in which you reflect on what you have learned and any difficulties you have encountered.
Occasional excursions to companies and construction sites give you a lively insight into the professional world of STEM graduates.
A short report must be prepared for each excursion for recognition.
If you would like to spend a little longer getting a taste of what STEM graduates do, you can complete a career orientation internship. The career orientation internship is offered in two variants: A shorter variant (4-5 days) for credit of 1 SWS and a longer variant (approx. 2 weeks) for credit of 2 SWS. It is possible to split the internship phase between several companies.
Documentation must be prepared for the vocational orientation internship.
Pre-course in mathematics
The preliminary course in mathematics usually takes place over several weeks before the start of lectures in the winter semester and mainly repeats the most important topics of school mathematics for the university. If you supplement your participation with a course credit, you can have the preliminary mathematics course credited to the MINT accompanying program.
This course, which is recommended for everyone, refreshes your mathematics knowledge from school, prepares you for the mathematics entrance test and reveals possible gaps that are then closed in the advanced mathematics course.
In order to receive credit for the MINT accompanying program (4 SWS), a course achievement in the form of written reflection tasks must be completed.
Chemistry preliminary course
The chemistry preliminary course usually takes place before the start of lectures in the winter semester and is an intensive course for important chemical basics. If you supplement your participation with coursework in the winter semester, you can receive credit for the chemistry preliminary course in the MINT accompanying program.
The chemistry preliminary course can be taken parallel to the mathematics preliminary course and is particularly recommended if you are interested in majoring in civil engineering, mechanical engineering, nanostructural sciences, physics and environmental engineering, as these majors include chemistry.
In order to receive credit for the MINT accompanying program (4 SWS), a course achievement in the form of successfully completed exercises must be provided.
Physics bridge course
The physics bridge course takes place for two hours each in the winter and summer semesters and primarily helps with problems in the Experimental Physics I and II lectures.
In order to receive credit for the MINT accompanying program (2 SWS per semester), a course achievement in the form of regular active participation must be achieved.
Physics for Engineers
This lecture plus tutorial offers a good repetition of basic physics at A-level plus, tailored to civil and environmental engineers.
Didactic physics seminar
This seminar takes place from the second half of the semester in the winter and summer semesters parallel to the lectures "Experimental Physics I" and "Experimental Physics II" for two hours and repeats the contents of the first half of the lecture "Experimental Physics" (in winter semester Mechanics, in summer semester Electricity) with a didactic focus.
MINT Thinking Sport
This new course, which was developed as part of the plusMINT degree program, aims to train logical thinking with puzzles from all areas of STEM.
Programming course Phython
An introduction to the Python programming language as part of the nanostructure sciences practical course and the advanced physical-chemical practical courses.