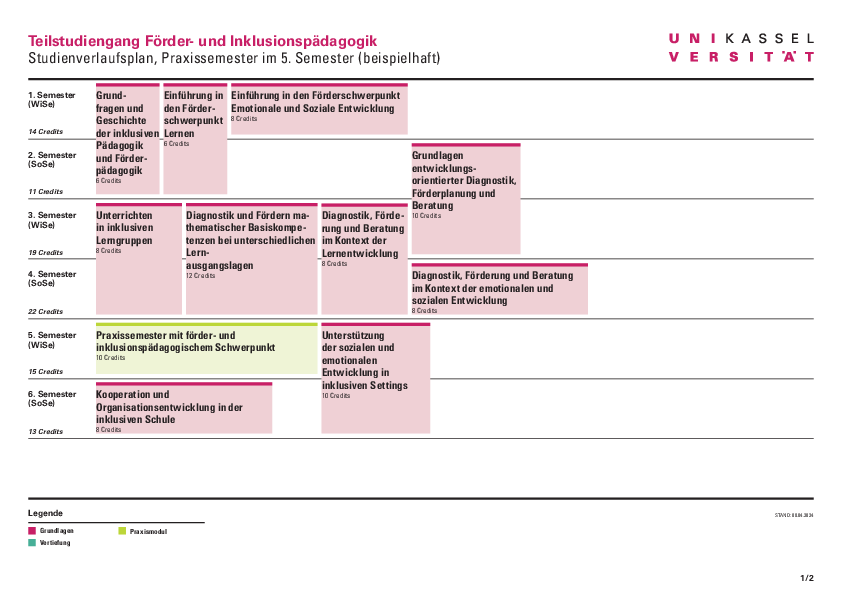
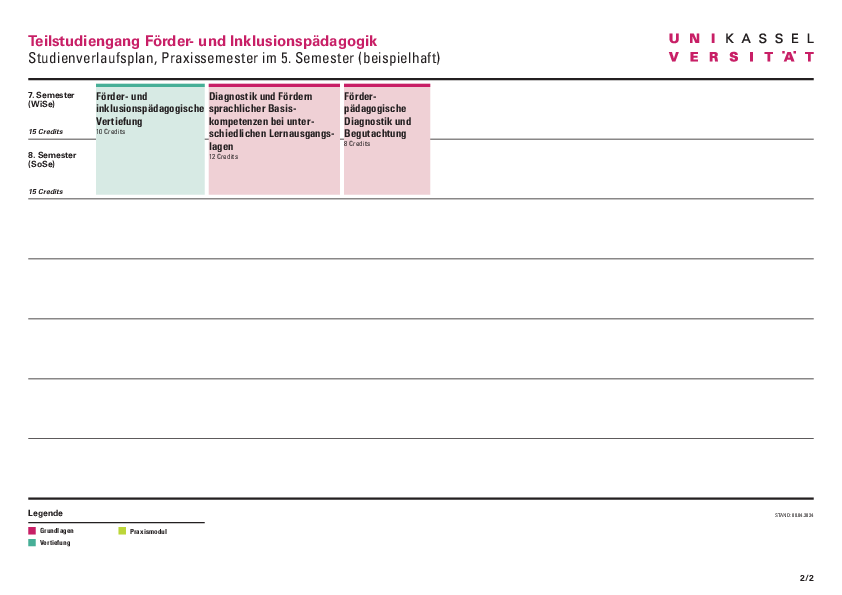
Study structure
The content on this page was translated automatically.
Course content
Students
- acquire knowledge of the historical development of special and special needs education
- deal with the relationship between special needs education and inclusive education
become familiar with models of the organization of special education and inclusive education and reflect on these critically in relation to the goals and methods of inclusive school development
- reflect on fundamental ethical issues in relation to heterogeneity, diversity and inclusion
- learn about didactic models for designing inclusive learning environments
- develop concepts and methods for monitoring, observing and documenting learning processes
- learn to analyze barriers to participation in classroom settings and reduce them through individual learning environments
After the basics, the in-depth module Support and inclusion pedagogy in-depth allows students to set an individual focus. Among other things, this module offers the opportunity to gain an insight into other areas of support (e.g. mental development, physical and motor development, hearing, vision), provided these are covered by the courses on offer.
Students
- acquire the basics of pedagogical observation, diagnostics and counseling
- learn about instruments for determining special educational needs and how to assess their significance
- learn how to create, implement and evaluate individual support plans
- acquire the skills to draw up reports to determine special educational needs, taking legal principles into account
acquire knowledge of the basics and areas of tension in counseling with regard to different target groups
Students
- carry out guided teaching experiments and reflect on their experiences in accompanying courses
- plan and design naturally differentiating learning opportunities for heterogeneous learning groups
- deal with the challenges of learning and interaction, taking individual learning requirements into account
- learn to appropriately justify didactic and methodological decisions from a support and inclusion pedagogical perspective
Funding priorities
In the specialization in learning, students acquire skills in the diagnosis, counselling and support of learning difficulties at school. Learning difficulties are seen as a symptom of complex problems that need to be addressed by involving various stakeholders (such as the children's families or other teachers).
Students
- acquire knowledge about explanatory factors for the development of learning difficulties
- learn about and reflect on didactic concepts to support the learning development of children and young people
- deal with relevant diagnostic methods and discuss their value for planning support and remedial measures
Integrated into the learning support focus, students acquire knowledge in the area of basic language and mathematical education. This enables them to support pupils at both primary and secondary level with regard to the necessary mathematical and linguistic basics.
Basic mathematical education
Students
- learn how mathematical learning works fundamentally and how students develop a central understanding of numbers, operations and calculation methods
- learn to assess the particular challenges of arithmetic learning processes
- develop the competence to assess individual learning levels in mathematics and to develop tasks with diagnostic and support potential
Basic linguistic education
Students
- acquire knowledge of the German language and writing system
- learn how monolingual and multilingual language acquisition and the development of writing and reading skills work
- develop the ability to recognize different levels of language development
- learn to assess the challenges of linguistic and literary learning processes
- develop the ability to identify individual learning levels in German and to develop tasks with diagnostic and support potential
In the Emotional and Social Development specialization, students acquire skills in diagnostics, counselling and support in the case of impairments in emotional and social development. Impairments in emotional and social development are seen as a symptom of complex problems that need to be addressed by involving various stakeholders (such as the children's families or other teachers).
Students
- become familiar with basic theories of social and emotional development in childhood and adolescence as well as the importance of peer relationships and educational relationships in the school context
- develop the ability to describe and analyze the manifestations and developmental conditions of impairments in emotional and social development
- develop the competence to design lessons taking into account approaches to emotional and social support
- become familiar with concepts and procedures for preventing and dealing with social problems and conflicts in the classroom