Study structure
This page contains automatically translated content.
General information
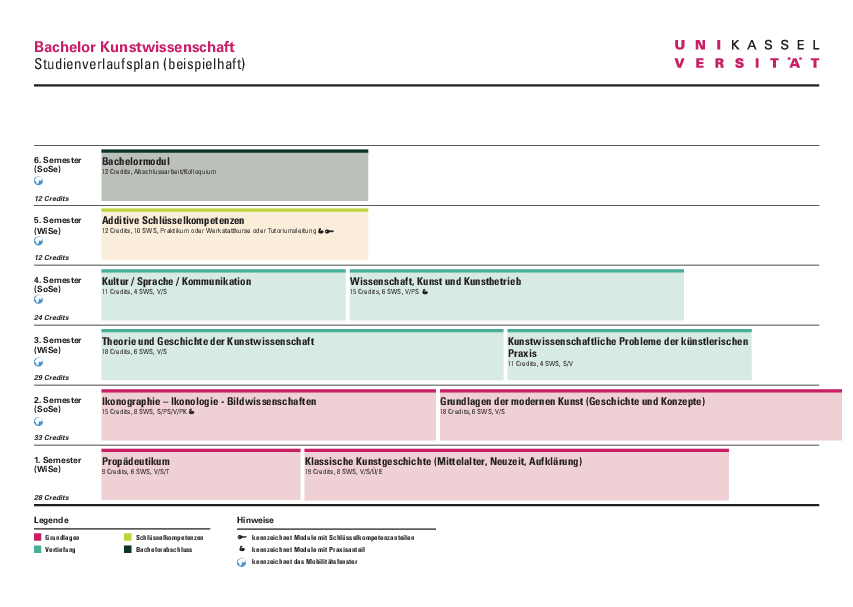
In the Bachelor's degree program in Art History , students acquire the basics of art historical work and research. They complete a total of ten modules, which are divided into four module groups: Introductory module I, foundation modules II to V and in-depth modules VI to IX. Bachelor module X concludes the course with the Bachelor thesis. The standard period of study for the Bachelor's degree in Art Studies at the University of Kassel is six semesters. Further information on the individual modules, their content and requirements can be found in the module handbook under Examination Regulations and Module Handbook.
Module I-V (introductory and basic modules)
The preparatory course is an introduction to the study of art history. It is compulsory for all art history students (major and minor subjects). Here they learn the basics of the developmental history of art, work analysis and art historical methodology.
Building on the foundations of the preparatory course, Module II deals with the study of art from the Middle Ages to the Enlightenment (around 1800). One focus is the analysis of works of art against the background of their dependence on the church, court and state and other art institutions such as the academies.
Module III deepens knowledge of art historical methodology. One focus is on iconography and iconology and art history as part of general visual studies.
In Module IV, students dedicate themselves to analyzing modern art and its central art theoretical debates. In doing so, reference to older art is of great importance in order to make lines of tradition in art and art theory across epochs visible.
Module V is dedicated to deepening knowledge of methods. To this end, the focus is on art studies and its exemplary texts and representatives.
Module VI-X (in-depth and final modules)
In Module VI, students focus on the diverse artistic processes and their art-scientific analysis. The aim is to examine works of art with a view to their respective production methods and materiality.
In Module VIII, students examine works of art in their dependence on the art business from modern times to the present. To this end, art criticism and the activities of public and private art institutions, e.g. the art trade and the publishing industry, as well as various forms of art promotion are examined.
Module IX comprises practical study formats. Students can choose one of three formats: They can complete an internship (e.g. in a museum, gallery, publishing house, etc.), take part in a workshop project at the art academy or lead a tutorial. In this way, students can gain insights into various professional fields in art history in this module.
The Bachelor's degree in Art Studies concludes with a Bachelor's thesis and accompanying colloquium. The Bachelor's degree qualifies students to take up a professional career and enables them to enter the Master's degree program.

Study and examination achievements
In order to complete a course, be it a lecture, a seminar or a project, students have to complete coursework and examinations. In addition to continuous participation in the course sessions, coursework can consist of presentations and minutes, for example. Examinations usually consist of term papers, but depending on the type of course, portfolios can also be developed, for example. Further information on coursework and examinations can be found in the module handbook atExamination regulations and module handbook.
Examination Office B.A. Art Studies
| Contact persons | Contact details |
|---|---|
Viktoria Wünsche-Cone Louise Knafla | Menzelstr. 13-15 Room 3320/Südbau E-mail: kuwiba[at]uni-kassel[dot]de |